Embark on a comprehensive exploration of the ATI Anatomy and Physiology 2009 Proctored Exam, an esteemed assessment designed to evaluate your mastery of the human body’s intricate systems. This examination not only tests your knowledge but also prepares you for success in healthcare professions.
Delve into the intricacies of the integumentary, skeletal, and muscular systems, unraveling their structures, functions, and roles in protection, movement, and support. Journey through the body’s cavities, deciphering the mechanisms of respiration, circulation, digestion, reproduction, and excretion.
Course Overview: Ati Anatomy And Physiology 2009 Proctored Exam
The ATI Anatomy and Physiology 2009 proctored exam is a comprehensive assessment of students’ knowledge of the human body and its functions. The exam covers a wide range of topics, including the structure and function of the major body systems, homeostasis, and fluid and electrolyte balance.
The exam format consists of multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, and short answer questions. Students are given 3 hours to complete the exam.
Body Systems
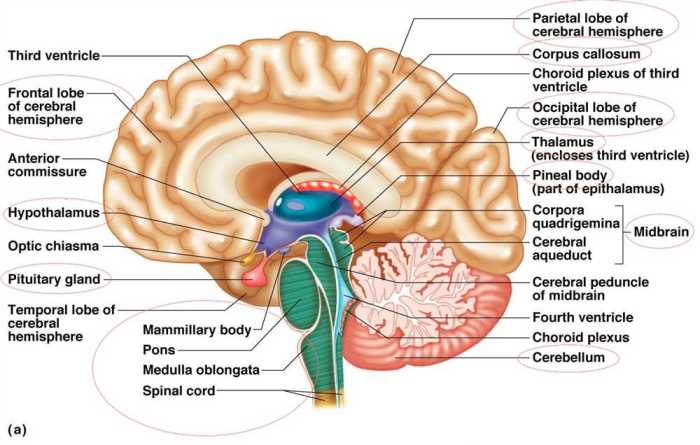
Integumentary System
The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body and consists of the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands. The skin is the body’s largest organ and serves as a protective barrier against the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and provides sensation.
Skeletal System, Ati anatomy and physiology 2009 proctored exam
The skeletal system consists of bones, joints, and muscles. Bones provide support and protection for the body, facilitate movement, and store minerals. Joints are the points of contact between bones and allow for movement.
Muscular System
The muscular system consists of skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and allow for voluntary movement. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of organs and blood vessels and control involuntary movements. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and contract to pump blood.
Body Cavities and Organs

Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity is located in the chest and contains the lungs, heart, and esophagus. The lungs are responsible for gas exchange, the heart pumps blood throughout the body, and the esophagus transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is located in the abdomen and contains the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas. The stomach digests food, the intestines absorb nutrients from food, the liver filters blood, and the pancreas produces digestive enzymes and hormones.
Pelvic Cavity
The pelvic cavity is located in the pelvis and contains the reproductive organs and urinary bladder. The reproductive organs produce gametes and hormones, and the urinary bladder stores urine.
Homeostasis

Body Fluid Balance
Body fluid balance is essential for maintaining homeostasis. The body takes in fluids through drinking and eating, and loses fluids through sweating, urination, and defecation. The kidneys help regulate body fluid balance by controlling the amount of water and electrolytes in the urine.
Temperature Regulation
Body temperature regulation is essential for maintaining homeostasis. The body produces heat through metabolism and loses heat through sweating, radiation, and convection. The hypothalamus helps regulate body temperature by controlling the body’s heat production and heat loss mechanisms.
pH Balance
pH balance is essential for maintaining homeostasis. The body maintains a pH of around 7.4 through the action of buffers, the respiratory system, and the renal system. Buffers neutralize acids and bases, the respiratory system removes carbon dioxide from the blood, and the renal system excretes acids and bases in the urine.
FAQ Corner
What is the format of the ATI Anatomy and Physiology 2009 Proctored Exam?
The exam consists of multiple-choice questions, true/false questions, and short answer questions.
What is the time limit for the exam?
The exam has a time limit of 3 hours.
What is the passing score for the exam?
The passing score for the exam is 75%.