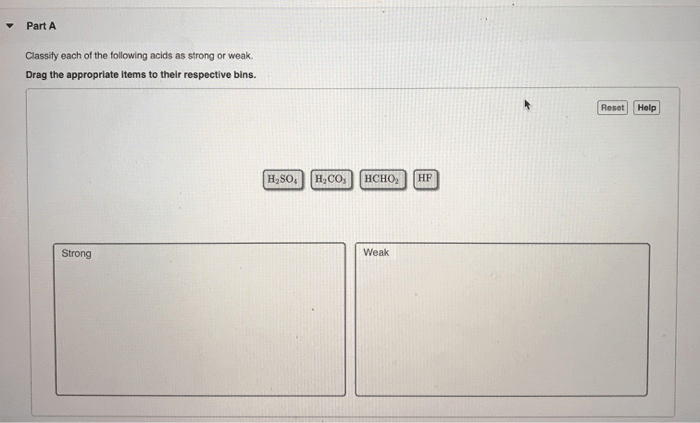
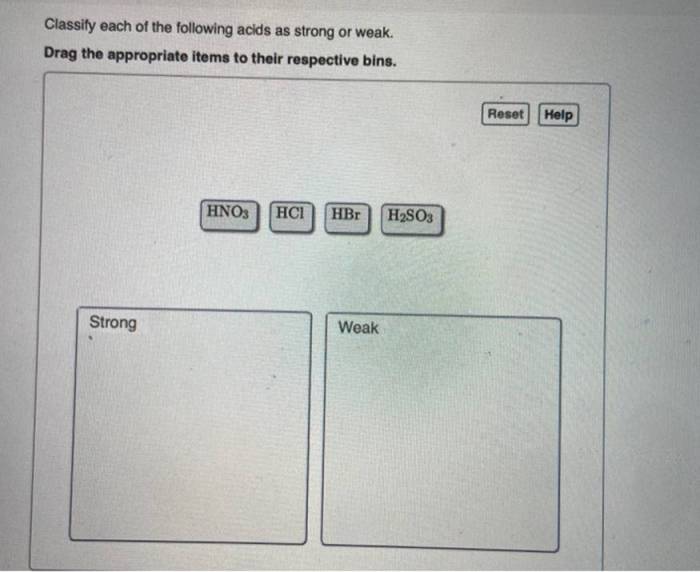
Classify each of the following acids as strong or weak. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of acids, exploring their properties, behaviors, and applications. By understanding the differences between strong and weak acids, we gain valuable insights into the chemical reactions and processes that shape our world.
Acids play a crucial role in various scientific disciplines, industrial processes, and everyday life. From the potent acids used in manufacturing to the milder acids found in household products, a thorough understanding of their strengths and characteristics is essential for safe handling, effective use, and scientific advancement.
Strong Acids
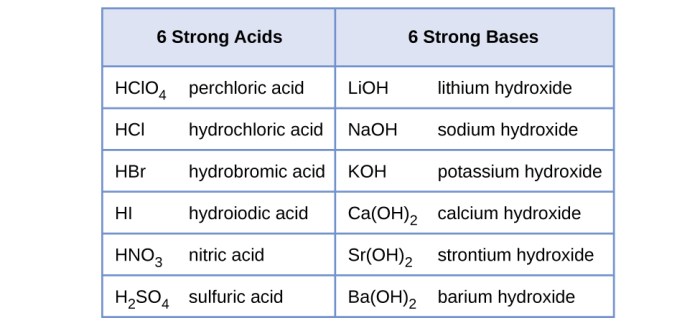
Strong acids are substances that completely dissociate in water, releasing all of their hydrogen ions (H+). They are characterized by their low pH values, typically below 2. Strong acids are highly corrosive and can cause severe burns and other injuries.
Characteristics of Strong Acids
- Completely dissociate in water
- Have low pH values
- Are highly corrosive
- Can cause severe burns and other injuries
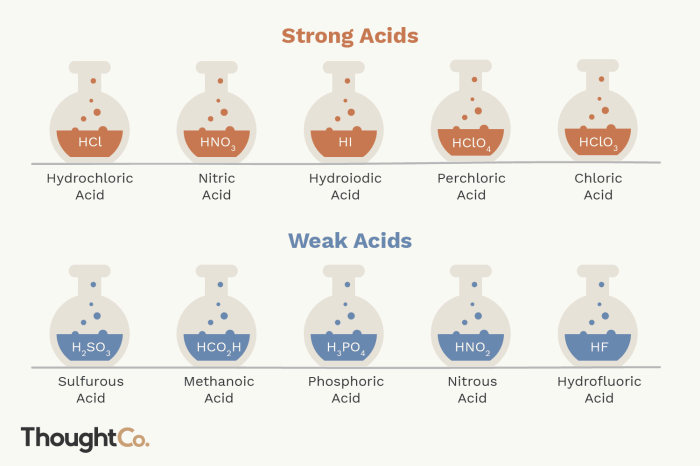
Examples of Strong Acids
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Nitric acid (HNO3)
Weak Acids: Classify Each Of The Following Acids As Strong Or Weak
Weak acids are substances that only partially dissociate in water, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions (H+). They are characterized by their higher pH values, typically between 2 and 7. Weak acids are less corrosive than strong acids and are generally safe to handle.
Characteristics of Weak Acids
- Partially dissociate in water
- Have higher pH values
- Are less corrosive
- Are generally safe to handle
Examples of Weak Acids
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
- Phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
Comparison of Strong and Weak Acids
Strong acids are much stronger than weak acids. They dissociate completely in water, releasing all of their hydrogen ions (H+), while weak acids only partially dissociate, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions (H+). This difference in dissociation strength is reflected in their pH values.
Strong acids have low pH values, typically below 2, while weak acids have higher pH values, typically between 2 and 7.
Differences in Dissociation Constants
The dissociation constant (Ka) is a measure of the strength of an acid. The higher the Ka, the stronger the acid. Strong acids have high Ka values, while weak acids have low Ka values.
Impact of Concentration on Acid Strength
The concentration of an acid can also affect its strength. The more concentrated an acid is, the stronger it is. This is because a more concentrated acid contains more hydrogen ions (H+).
Applications of Strong and Weak Acids
Strong acids are used in a wide variety of industrial applications, including the production of fertilizers, dyes, and plastics. They are also used in batteries and as cleaning agents.
Weak acids are used in a variety of everyday applications, including food and beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. They are also used in agriculture and as cleaning agents.
Examples of Products that Contain Strong or Weak Acids
- Strong acids: hydrochloric acid (HCl) is used in the production of fertilizers and plastics; sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used in the production of batteries and cleaning agents
- Weak acids: acetic acid (CH3COOH) is used in vinegar and salad dressings; carbonic acid (H2CO3) is used in carbonated beverages; phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is used in fertilizers and cleaning agents
Safety Considerations
Strong acids are highly corrosive and can cause severe burns and other injuries. It is important to take precautions when handling strong acids, including wearing protective clothing, gloves, and goggles.
Weak acids are less corrosive than strong acids, but they can still cause skin irritation and other injuries. It is important to avoid contact with weak acids, especially if you have sensitive skin.
Precautions to Take When Working with Acids
- Wear protective clothing, gloves, and goggles
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes
- Handle acids in a well-ventilated area
- Dispose of acids properly
Tips for Safe Storage and Disposal of Acids, Classify each of the following acids as strong or weak
- Store acids in a cool, dry place
- Keep acids away from children and pets
- Dispose of acids according to local regulations
Question & Answer Hub
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
Strong acids dissociate completely in water, releasing all of their hydrogen ions (H+). Weak acids dissociate only partially, releasing only a small fraction of their hydrogen ions.
What are some examples of strong acids?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3) are common examples of strong acids.
What are some examples of weak acids?
Acetic acid (CH3COOH), carbonic acid (H2CO3), and hydrofluoric acid (HF) are examples of weak acids.