Bioflix activity gas exchange the respiratory system – As we embark on a journey into the depths of the Bioflix activity on gas exchange within the respiratory system, let us prepare ourselves for an immersive exploration that unravels the intricacies of this vital process. This endeavor promises to illuminate the remarkable mechanisms that govern the exchange of gases between our bodies and the environment, providing a profound understanding of the fundamental principles that sustain life itself.
Delving into the anatomy of the respiratory system, we will uncover the intricate structures that orchestrate gas exchange, including the lungs, airways, and diaphragm. We will trace the fascinating pathway of air as it traverses the respiratory system, embarking on a journey of transformation that culminates in the vital exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Introduction
BioFlix activity gas exchange explores the respiratory system, a complex network of organs responsible for facilitating the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The respiratory system plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring an adequate supply of oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration.
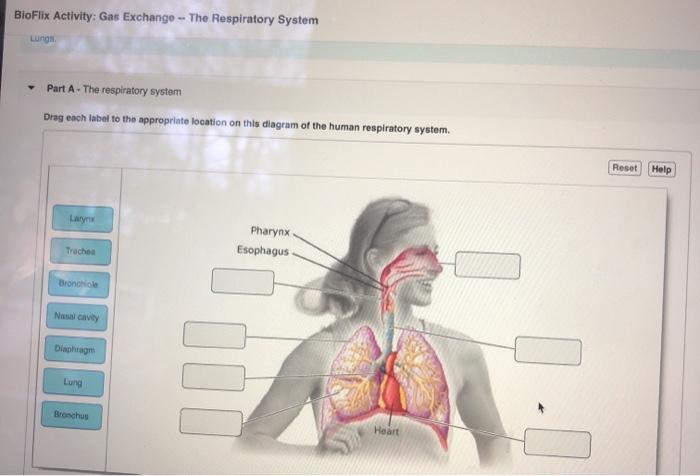
Anatomy of the Respiratory System: Bioflix Activity Gas Exchange The Respiratory System
The respiratory system consists of several key structures:
- Lungs:The primary organs of gas exchange, the lungs are composed of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
- Airways:A series of tubes, including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, which conduct air to and from the lungs.
- Diaphragm:A large muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and plays a crucial role in breathing.
Air enters the respiratory system through the nose or mouth and travels through the airways to the lungs. In the lungs, the alveoli are surrounded by capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, where gas exchange takes place.
Gas Exchange Process
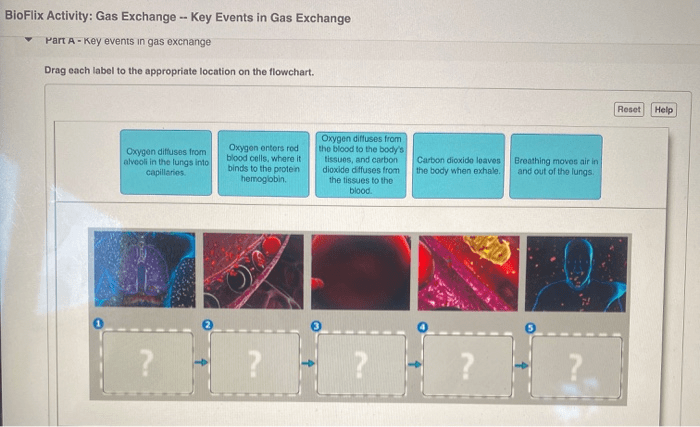
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the lungs and the bloodstream. This process is driven by diffusion, the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the capillaries, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli. This exchange is facilitated by the thin walls of the alveoli and capillaries, which allow for efficient diffusion.
Regulation of Respiration
Respiration is regulated by a complex interplay of nervous and chemical factors.
The respiratory center in the brainstem controls the rate and depth of breathing. It monitors blood pH, oxygen levels, and carbon dioxide levels, and adjusts breathing accordingly.
Chemical factors, such as changes in blood pH, can also affect respiration. For example, an increase in blood acidity can stimulate breathing to increase oxygen intake and remove carbon dioxide.
Respiratory Adaptations

The respiratory system adapts to meet the varying demands of different environments and activities.
At high altitudes, where oxygen levels are lower, the respiratory system increases breathing rate and depth to maintain oxygen levels.
During exercise, the respiratory system increases breathing rate and depth to meet the increased oxygen demands of the muscles.
General Inquiries
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment, ensuring a continuous supply of oxygen to the cells and the removal of carbon dioxide.
How does gas exchange occur in the lungs?
Gas exchange in the lungs occurs through a process called diffusion, where oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the thin walls of the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be exhaled.
What factors regulate the rate and depth of breathing?
The rate and depth of breathing are regulated by a complex interplay of neural and chemical factors, including the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood, as well as signals from the brain’s respiratory center.
How does the respiratory system adapt to different environmental conditions?
The respiratory system exhibits remarkable adaptability to varying environmental conditions, such as altitude and exercise. At high altitudes, the body increases the rate and depth of breathing to compensate for the reduced oxygen availability. During exercise, the respiratory system adjusts to meet the increased metabolic demands, delivering more oxygen to the muscles.