Classify the actions as either discretionary spending or automatic stabilizers. Discretionary spending is spending that the government chooses to make, while automatic stabilizers are spending that is triggered by changes in the economy. Both types of spending can have a significant impact on the economy, and it is important to understand the difference between them.
Discretionary spending is spending that the government chooses to make, regardless of the state of the economy. This type of spending includes things like infrastructure projects, education, and healthcare. Automatic stabilizers, on the other hand, are spending that is triggered by changes in the economy.
For example, unemployment benefits are an automatic stabilizer that increases when the unemployment rate rises.
Discretionary Spending

Discretionary spending refers to government expenditures that are not mandatory and can be adjusted based on economic conditions and policy priorities. These expenditures are typically used to fund programs and services that are not essential for the functioning of the government, such as infrastructure projects, education, and healthcare.
Examples of discretionary spending include:
- Infrastructure projects, such as road construction and bridge repair
- Education programs, such as funding for public schools and universities
- Healthcare programs, such as Medicaid and Medicare
- Social welfare programs, such as food stamps and housing assistance
- Defense spending
Discretionary spending can impact the economy in several ways:
- Economic growth:Increased discretionary spending can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs and boosting demand for goods and services.
- Inflation:Excessive discretionary spending can lead to inflation if the economy is already operating at full capacity.
- Government debt:Discretionary spending is often financed through borrowing, which can increase government debt levels.
Automatic Stabilizers

Automatic stabilizers are government policies that automatically adjust to changes in the economy without the need for legislative action. These policies are designed to stabilize the economy by reducing the impact of economic fluctuations.
Automatic stabilizers differ from discretionary spending in that they are not subject to the political process and are triggered by economic conditions rather than policy decisions.
The role of automatic stabilizers is to:
- Reduce the severity of economic downturns:Automatic stabilizers provide support to individuals and businesses during economic downturns, helping to maintain demand and prevent a deep recession.
- Mitigate the impact of economic booms:Automatic stabilizers can help prevent the economy from overheating during economic booms by reducing the amount of money in circulation.
Classifying Actions
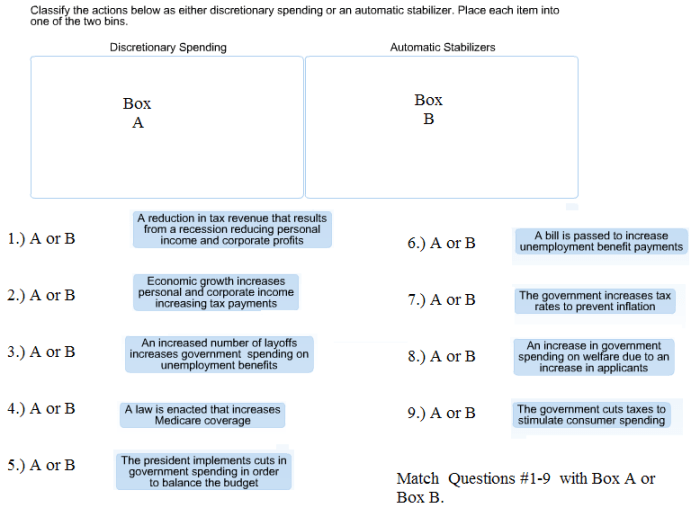
| Action | Discretionary Spending | Automatic Stabilizers | Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure project | Yes | No | Requires legislative approval |
| Unemployment benefits | No | Yes | Triggered by economic conditions |
| Education funding | Yes | No | Subject to political process |
| Tax refunds | No | Yes | Adjusts automatically to changes in income |
Impact on Economic Stability
Discretionary spending and automatic stabilizers play different roles in maintaining economic stability:
- Discretionary spending:Discretionary spending can be used to stimulate the economy during economic downturns and reduce inflation during economic booms. However, it can also lead to increased government debt and inflation if not managed carefully.
- Automatic stabilizers:Automatic stabilizers provide a more immediate and automatic response to economic fluctuations. They help to stabilize the economy by reducing the severity of economic downturns and mitigating the impact of economic booms.
The combination of discretionary spending and automatic stabilizers can help maintain a stable economy by providing a flexible and responsive fiscal policy.
Historical examples of the use of discretionary spending and automatic stabilizers to stabilize the economy include:
- The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009:This discretionary spending package was used to stimulate the economy during the Great Recession.
- The unemployment insurance system:This automatic stabilizer provides benefits to unemployed workers, helping to maintain consumer spending during economic downturns.
Policy Implications: Classify The Actions As Either Discretionary Spending Or Automatic Stabilizers
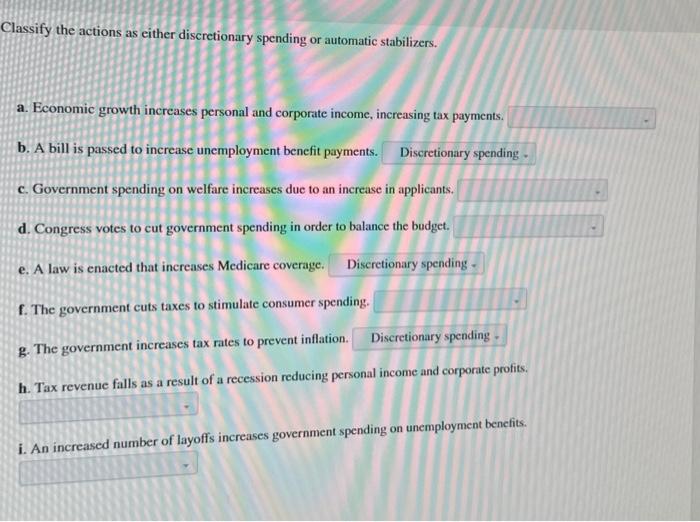
The classification of actions as discretionary spending or automatic stabilizers has important policy implications:
- Government management:The government has a role in managing both discretionary spending and automatic stabilizers to ensure that they are used effectively to stabilize the economy.
- Policy decisions:The classification of actions can inform policy decisions related to economic stability. For example, the government may choose to increase discretionary spending during economic downturns or adjust automatic stabilizers to respond to changing economic conditions.
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between discretionary spending and automatic stabilizers?
Discretionary spending is spending that the government chooses to make, while automatic stabilizers are spending that is triggered by changes in the economy.
How do automatic stabilizers help to stabilize the economy?
Automatic stabilizers help to stabilize the economy by increasing spending during a recession and decreasing spending during a boom.