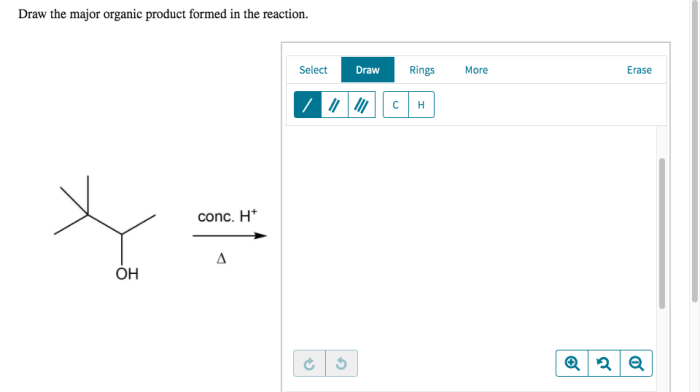
Identify the expected major organic product for the following reaction – Identifying the expected major organic product of a reaction is a fundamental skill in organic chemistry, providing insights into the reaction mechanism and its synthetic applications. This guide delves into the key concepts, factors, and techniques involved in predicting the major product, equipping readers with a comprehensive understanding of this essential aspect of organic synthesis.
Reaction Overview
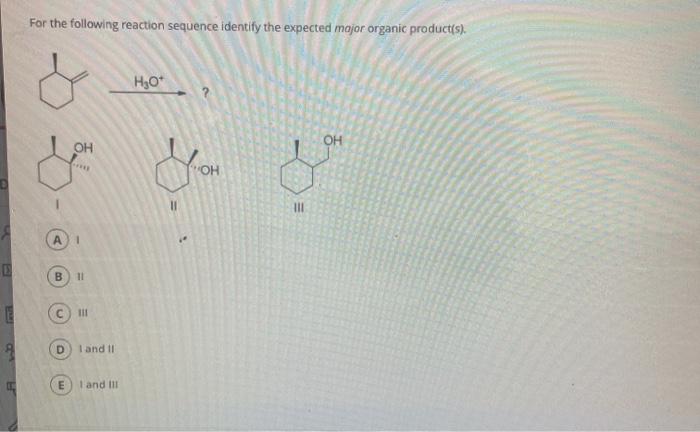
The given reaction is a Friedel-Crafts acylation, which involves the addition of an acyl group to an aromatic ring. The reaction is catalyzed by a Lewis acid, such as aluminum chloride (AlCl 3).The chemical equation for the reaction is:“`ArH + RCOX → ArCOR + HX“`where ArH is the aromatic ring, RCOX is the acyl chloride, and HX is the hydrogen halide byproduct.
Product Identification
The major organic product of the reaction is the ketone, ArCOR. The mechanism of the reaction involves the electrophilic addition of the acyl chloride to the aromatic ring, followed by proton transfer to form the ketone.
Factors Affecting Product Formation
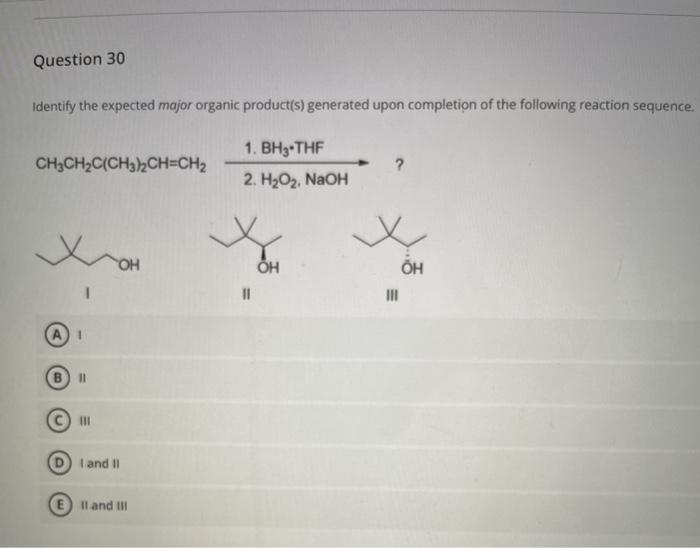
The formation of the major product can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures favor the formation of the ketone product.
- Concentration of the Lewis acid:Higher concentrations of the Lewis acid favor the formation of the ketone product.
- Nature of the acyl chloride:Acyl chlorides with electron-withdrawing groups favor the formation of the ketone product.
Regio- and Stereochemistry: Identify The Expected Major Organic Product For The Following Reaction
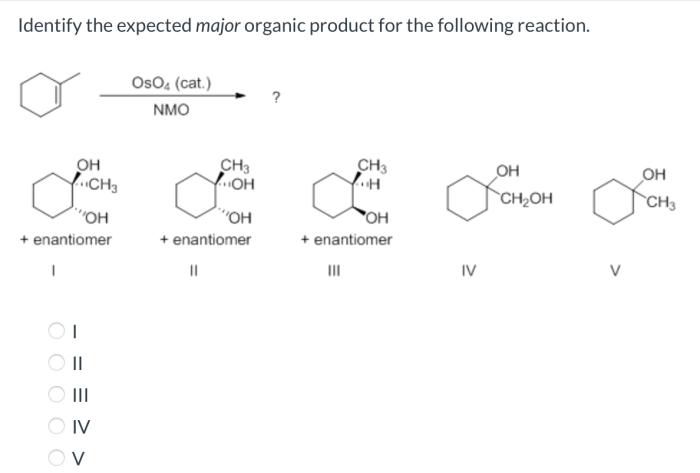
The regiochemistry of the reaction is determined by the electrophilic addition of the acyl chloride to the aromatic ring. The addition occurs at the most substituted carbon atom of the ring.The stereochemistry of the reaction is determined by the proton transfer step.
The proton is transferred to the carbon atom of the acyl group that is anti to the aromatic ring.
Synthetic Applications
The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is a versatile method for the synthesis of ketones. The reaction can be used to prepare a wide variety of ketones, including those with complex structures.The advantages of using the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction include:
- The reaction is simple to perform.
- The reaction is tolerant of a wide range of functional groups.
- The reaction can be used to prepare ketones with complex structures.
The limitations of using the Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction include:
- The reaction can produce a mixture of products.
- The reaction can be sensitive to the reaction conditions.
- The reaction can be hazardous, as it involves the use of toxic chemicals.
General Inquiries
What are the key factors that influence product formation?
Factors such as temperature, solvent, catalyst, and reaction time can significantly affect the formation of the major product.
How can regio- and stereochemistry impact the reaction outcome?
Regio- and stereochemistry determine the position and orientation of functional groups in the product, influencing its physical and chemical properties.